Atomic mass and atomic number may have similarities, but they are used to revealing different characteristics of elements. According to the definitions given, atomic mass which is also called atomic weight is the measured total mass of an element’s atom. This two minute video shows how to read the periodic table. The terms 'atomic number' and 'atomic mass' are also defined. Find more free tutorials, videos.
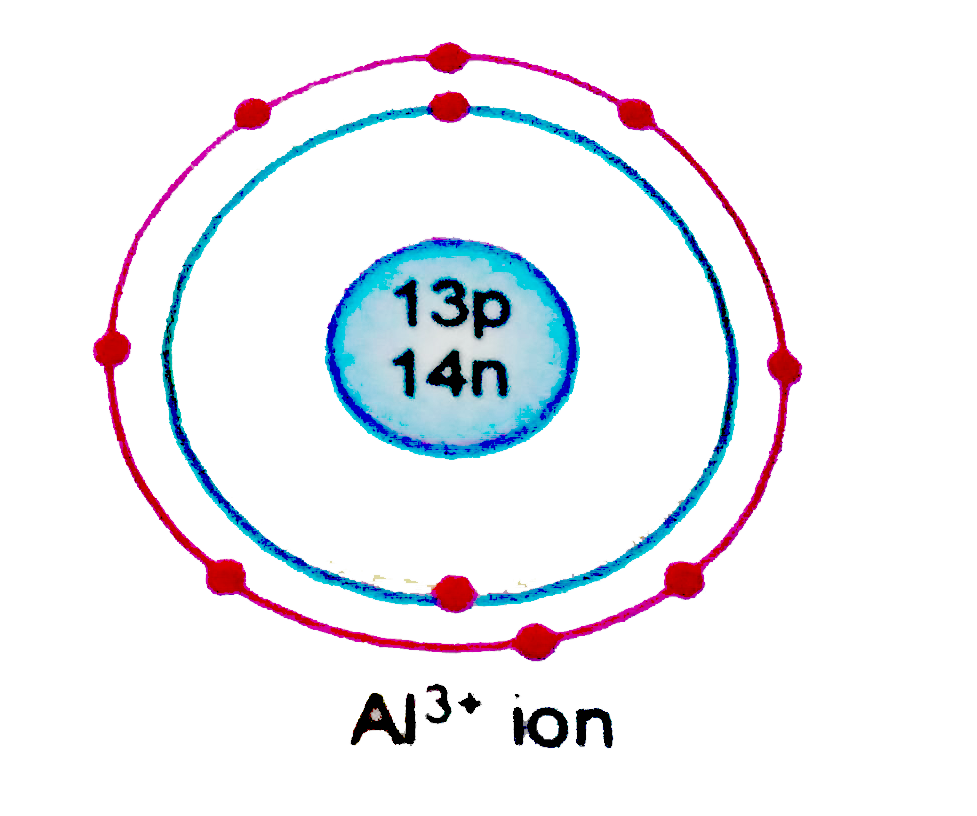
Atomic number or proton number is defined as the total number of protons in the nucleus. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the atomic number. Atomic Number The atomic number or proton number is defined as the total number of protons in the nucleus and is given the symbol Z. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the atomic number. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze. Atomic number or proton number is defined as the total number of protons in the nucleus. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the atomic number.
The atomic number (symbol: Z) of an atom is the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.[1][2] The atomic number of an atom identifies which element it is. In a neutral atom, the atomic number is equal to the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus.[1] The elements of the periodic table are listed in order of increasing atomic number.[2]
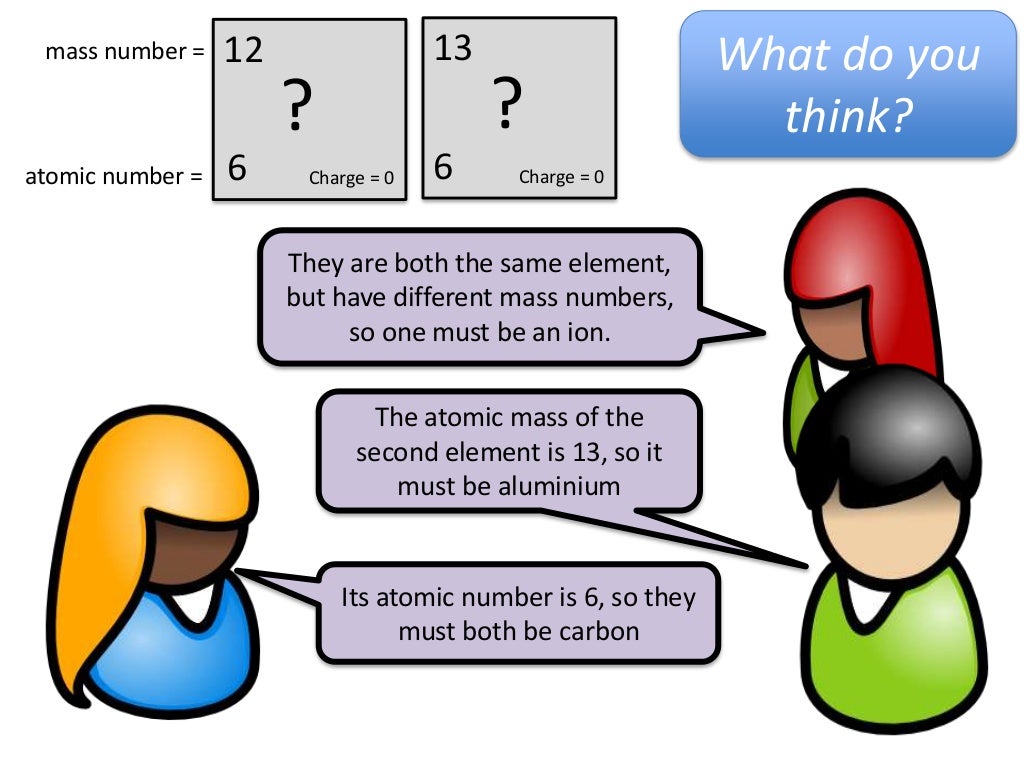
Atomic number is not the same as:
- atomic mass (symbol: ma), which is the mass of a single atom, commonly expressed in unified atomic mass units
- mass number (symbol: A), which is the sum of the number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
- relative atomic mass (also called atomic weight;symbol: Ar), which is the ratio of the average mass per atom of an element from a given sample to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
The atomic number of the periodic table directly corresponds to the number of protons which is in the atom. Once another proton is added, it is no longer the same element. The same cannot be applied to when another neutron or another electron is added. Adding more electrons will give the atom a negative charge and removing electrons will give the atom a positive charge. Metals tend to lose electrons, which creates a positive charge. Non-metals tend to gain electrons, forming a negative charge. Electrons are the foundation for determining how compounds are formed amongst atoms. Adding or removing neutrons within an atom changes its isotope. As an example, carbon-12 is the most stable isotope for a carbon atom. However, we can add two more neutrons and carbon-12 is now carbon-14, a less stable isotope of carbon. The number of an isotope directly correlates to the atomic mass of an element. The amount of neutrons in any given atom by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass.
References[change | change source]
- ↑ 1.01.1Daintith, John, ed. (2008). A Dictionary of Chemistry (Sixth ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 48. ISBN978-0-19-920463-2.
- ↑ 2.02.1Moore, John T. (2010). Chemistry Essentials For Dummies. Wiley. p. 36. ISBN978-0-470-61836-3.
Related pages[change | change source]
Atomic Number Is What

Atomic Number Is 14
Atomic Number Is Equal To




